Which option is best depends on the stage of the disease, the Gleason score, and the PSA level. Other important factors are age, general health, and a person's views about potential treatments and their possible side effects. Because all treatments can have significant side effects, such as erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence, treatment discussions often focus on balancing the goals of therapy with the risks of lifestyle alterations. A combination of the treatment options is often recommended for managing prostate cancer.
Guidelines for treatment for specific clinical situations requires a good estimation of a person's long-term life expectancy. People can also use an 18-item questionnaire to learn whether they have good knowledge and understanding about their treatment options before they choose. Most of those who are newly diagnosed and made a treatment choice can not correctly answer over half of the questions.
If radiation therapy is done first, and fails, then radical prostatectomy is very technically challenging surgery and may not be feasible. On the other hand, radiation therapy done after surgical failure may have many complications.
In localized disease it is unknown if radical prostatectomy is better or worse than watchful waiting.
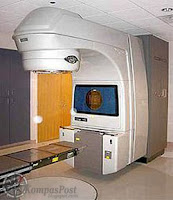
The selection of treatment options may be a complex decision involving many factors. For example, radical prostatectomy after primary radiation failure is a very technically challenging surgery and may not be an option. This may enter into the treatment decision.
If the cancer has spread beyond the prostate, treatment options significantly change, so most doctors that treat prostate cancer use a variety of nomograms to predict the probability of spread. Treatment by watchful waiting/active surveillance, HIFU, external beam radiation therapy, brachytherapy, cryosurgery, and surgery are, in general, offered to men whose cancer remains within the prostate. Hormonal therapy and chemotherapy are often reserved for disease that has spread beyond the prostate. However, there are exceptions: Radiation therapy may be used for some advanced tumors, and hormonal therapy is used for some early stage tumors. Cryotherapy (the process of freezing the tumor), hormonal therapy, and chemotherapy may also be offered if initial treatment fails and the cancer progresses.
Source: Wikipedia
License: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License




0 comments:
Posting Komentar